The Ultimate Guide to Marketing in Manufacturing
Oct 28, 2024

Introductions
The manufacturing industry is at a pivotal crossroads. With the rapid advancement of technology, globalization of markets, and the increasing demands of a digitally savvy customer base, manufacturing companies must rethink their marketing strategies to stay competitive. Traditional methods that once dominated the industry, such as trade shows, print ads, and direct sales, are no longer sufficient on their own. The modern manufacturing landscape requires a multifaceted approach that leverages digital channels, data analytics, and customer-centric strategies.
This comprehensive guide delves deep into the intricacies of marketing within the manufacturing sector. It offers actionable insights and practical strategies designed to help manufacturing companies of all sizes enhance their marketing efforts. From understanding the modern buyer’s journey to leveraging cutting-edge technologies like AI and IoT, this guide covers every aspect necessary to transform your marketing approach and drive sustainable growth.
Chapter 1: Understanding the Modern Manufacturing Market.

1.1 The Transformation of Manufacturing Marketing
The Decline of Traditional Marketing Methods
• Trade Shows and Conferences: Historically, trade shows have been a cornerstone of manufacturing marketing. They provided a platform for networking, showcasing products, and establishing industry presence. However, their reach is limited geographically and temporally. The costs associated with participation—booth setup, logistics, travel, and accommodation—can be prohibitive, especially for smaller companies. Additionally, the COVID-19 pandemic highlighted the vulnerability of relying solely on in-person events, leading to cancellations and reduced attendance.
• Print Advertising: Once a dominant force in marketing, print media has seen a significant decline due to the rise of digital content consumption. Ads in industry-specific magazines and newspapers no longer guarantee the exposure they once did. Measuring the effectiveness of print ads is challenging, making it difficult to justify the investment without clear ROI metrics.
• Cold Calling and Direct Mail: These outbound marketing strategies often yield low response rates. Decision-makers are inundated with unsolicited communications and have become adept at filtering them out. Moreover, regulatory changes like the GDPR have imposed stricter rules on unsolicited outreach, increasing the risk of non-compliance penalties.
The Rise of Digital Marketing in Manufacturing
• Online Presence as a Necessity: In the digital age, a company’s website is its storefront. Potential clients conduct online research before engaging with suppliers, making a professional and informative website critical. Social media platforms offer additional channels to reach and engage with audiences, humanizing the brand and fostering community.
• Content Marketing’s Growing Importance: By creating valuable content—such as blog posts, whitepapers, and videos—manufacturing companies can establish thought leadership and build trust with potential clients. Educational content helps prospects understand complex products or services, positioning your company as an industry expert.
• Data-Driven Strategies and Personalization: Digital marketing allows for precise targeting based on data analytics. Companies can personalize marketing messages to specific segments, improving engagement rates. Tools like CRM systems and marketing automation software enable tracking of customer interactions, providing insights to refine strategies continually.
1.2 Globalization and Its Impact on Marketing
Opportunities and Challenges of Global Markets
• Expanded Customer Base: Globalization opens doors to new markets, diversifying revenue streams and reducing dependency on local economies. Access to emerging markets can lead to significant growth opportunities.
• Increased Competition: Alongside opportunities, globalization introduces more competitors, including low-cost manufacturers from countries with cheaper labor. Differentiating your offerings becomes crucial to maintain a competitive edge.
Adapting Marketing Strategies for a Global Audience
• Localization: Adapting marketing materials to reflect local languages, cultures, and preferences is essential. This goes beyond mere translation—it involves understanding local customs, idioms, and cultural nuances to ensure your message resonates.
• Cultural Sensitivity and Awareness: Missteps in cultural understanding can damage your brand’s reputation. For example, certain colors, symbols, or phrases may have different connotations in different cultures. Conducting thorough market research or partnering with local agencies can help avoid these pitfalls.
• Regulatory Compliance: Each country has its own set of regulations concerning advertising, data protection, and industry-specific standards. Non-compliance can result in legal consequences and erode customer trust. It’s imperative to understand and adhere to these regulations when entering new markets.
1.3 The Digital-Savvy Customer
Changing Buyer Behavior in B2B Manufacturing
• Self-Education and Research: Modern buyers prefer to conduct extensive online research before contacting suppliers. They rely on digital content to compare solutions, read reviews, and gather information, often making up to 70% of their buying decision before engaging with sales representatives.
• Demand for Personalization and Immediate Gratification: Customers expect interactions tailored to their specific needs and challenges. They are accustomed to the immediacy of information in the digital age and expect quick responses to inquiries.
• Preference for Multi-Channel Engagement: Buyers interact with brands across multiple touchpoints—websites, social media, email, and more. They expect a seamless experience regardless of the channel, making omnichannel marketing strategies essential.
Implications for Manufacturers
• Enhanced Online Visibility: Investing in SEO and content marketing is critical to ensure your company appears in search results when potential clients are seeking solutions. This includes optimizing for keywords relevant to your industry and audience.
• Interactive and Responsive Communication: Implementing live chat features, chatbots, and prompt email responses meets customers’ demands for immediate engagement. These tools can answer frequently asked questions, guide users through your website, and even qualify leads.
• Leveraging Testimonials and Case Studies: Social proof is powerful. Sharing success stories and customer testimonials builds credibility and trust. Video testimonials, in particular, can be highly persuasive.
Chapter 2: Identifying and Understanding Your Target Audience

2.1 Building Comprehensive Buyer Personas
The Importance of Buyer Personas
Buyer personas are semi-fictional representations of your ideal customers based on real data and market research. They help you understand your customers better, allowing you to tailor your marketing efforts to the specific needs, behaviors, and concerns of different segments.
Components of a Buyer Persona
• Demographics: Age, gender, education level, and location can influence purchasing behavior.
• Firmographics: Company size, industry sector, annual revenue, and market position provide context about the organizational environment.
• Roles and Responsibilities: Understanding job titles, daily responsibilities, and challenges helps tailor messaging to address specific pain points.
• Goals and Objectives: Identifying what success looks like for your customers enables you to align your solutions with their objectives.
• Challenges and Pain Points: Recognizing the obstacles your customers face allows you to position your offerings as solutions.
• Preferred Communication Channels: Knowing whether your audience prefers email, phone calls, or social media ensures your messages reach them effectively.
Steps to Create Buyer Personas
1. Conduct Qualitative and Quantitative Research: Use surveys, interviews, and analytics data to gather insights. Engage with your sales and customer service teams who interact directly with customers.
2. Identify Patterns and Trends: Look for commonalities in the data that indicate shared characteristics or behaviors.
3. Develop Detailed Persona Profiles: Create narratives that include a name, background, and a day-in-the-life scenario. This humanizes the persona and makes it easier for your team to empathize with them.
4. Use Personas to Inform Marketing Strategies: Tailor your content, messaging, and channels to each persona.
5. Review and Update Regularly: Markets evolve, and so do your customers. Regularly revisit your personas to ensure they remain accurate.
2.2 Market Segmentation Strategies
Benefits of Market Segmentation
Market segmentation allows you to focus your marketing efforts on specific groups, increasing efficiency and effectiveness. It helps in:
• Personalizing Marketing Messages: Tailoring messages to resonate with each segment’s unique needs.
• Optimizing Resource Allocation: Focusing on the most profitable or high-potential segments.
• Enhancing Customer Satisfaction: Providing solutions that closely align with customer expectations.
Types of Segmentation
• Geographic Segmentation: Dividing the market based on location, which is useful for regional marketing strategies and understanding local competition.
• Demographic Segmentation: Grouping customers by industry, company size, or job function.
• Behavioral Segmentation: Categorizing based on purchasing behavior, usage rate, brand loyalty, or benefits sought.
• Psychographic Segmentation: Considering customers’ values, attitudes, and lifestyle choices.
Implementing Segmentation
1. Data Collection: Use CRM systems, website analytics, and customer surveys to gather data.
2. Analyze and Identify Segments: Employ statistical methods and software to detect patterns.
3. Develop Segment Profiles: Describe each segment’s characteristics, needs, and preferences.
4. Tailor Marketing Strategies: Customize product offerings, messaging, and channels for each segment.
5. Monitor and Adjust: Continuously track performance and adapt strategies based on results.
2.3 Competitor Analysis
The Role of Competitor Analysis in Marketing
Competitor analysis helps you understand the market landscape, identify opportunities, and benchmark your performance. It provides insights into:
• Competitors’ Strengths and Weaknesses: Understanding where they excel or fall short.
• Market Positioning: Recognizing how competitors position themselves and how you can differentiate.
• Customer Perceptions: Gleaning insights from competitor reviews and customer feedback.
Steps in Competitor Analysis
1. Identify Competitors: List direct competitors offering similar products and services, and indirect competitors addressing the same customer needs differently.
2. Research Competitor Offerings: Analyze their product features, pricing models, service quality, and innovation levels.
3. Examine Marketing Strategies: Look at their branding, messaging, advertising channels, and customer engagement practices.
4. Assess Market Share and Financials: Where possible, review their market penetration and financial health.
5. Perform a SWOT Analysis: Evaluate their strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
Leveraging Insights
• Differentiation: Identify unique selling propositions that set you apart.
• Market Gaps: Spot unmet customer needs or underserved segments.
• Best Practices: Learn from competitors’ successful strategies and avoid their mistakes.
Chapter 3: Crafting a Powerful Brand Identity

3.1 Defining Your Brand’s Core
The Essence of a Strong Brand
A strong brand communicates your company’s identity, values, and promise to customers. It builds recognition and trust, influencing purchasing decisions.
Developing Your Mission Statement
• Purpose-Driven Articulation: Define what your company does, for whom, and the value it provides.
• Clarity and Simplicity: Avoid jargon; make it understandable to all stakeholders.
• Alignment with Actions: Ensure that company activities reflect the mission to maintain credibility.
Crafting a Vision Statement
• Aspirational Outlook: Describe the future state you aim to achieve.
• Inspirational Tone: Motivate employees and stakeholders with a compelling vision.
• Guiding Principle: Use it as a roadmap for strategic planning and decision-making.
Establishing Core Values
• Authenticity: Reflect genuine beliefs and practices.
• Behavioral Guideposts: Influence company culture and employee conduct.
• Decision-Making Framework: Aid in evaluating strategies and initiatives for alignment with values.
3.2 Visual Identity Elements
The Importance of Visual Branding
Visual branding creates immediate recognition and conveys professionalism. Consistency across all visual elements reinforces brand identity.
Designing an Effective Logo
• Simplicity and Memorability: A clean, simple design is easier to recognize and recall.
• Relevance: The logo should reflect the nature of your business.
• Versatility: Ensure it looks good in various formats—digital, print, large banners, or small promotional items.
• Color and Typography Harmony: The logo’s colors and fonts should align with the overall brand aesthetic.
Choosing a Color Palette
• Psychological Impact: Colors evoke emotions and associations.
• Red: Energy, passion, urgency.
• Blue: Trust, reliability, professionalism.
• Green: Growth, sustainability, health.
• Cultural Sensitivity: Be aware of color meanings in different cultures to avoid misinterpretation.
Typography and Imagery
• Font Selection: Choose fonts that are legible and reflect your brand’s personality—whether modern, traditional, or innovative.
• Consistent Imagery Style: Use a coherent style for photographs and graphics to maintain a unified look.
3.3 Brand Voice and Messaging
Establishing a Consistent Brand Voice
Your brand voice should be consistent across all communications, embodying your company’s personality.
• Tone: Decide if your tone is formal, conversational, authoritative, or friendly.
• Language Style: Balance technical accuracy with accessibility, avoiding jargon when communicating with non-expert audiences.
• Storytelling Techniques: Use narratives to engage audiences emotionally.
Key Messaging Pillars
• Quality and Reliability: Emphasize adherence to industry standards, certifications, and rigorous quality control processes.
• Innovation and Technology: Highlight your commitment to research and development, showcasing cutting-edge technologies.
• Customer-Centric Approach: Demonstrate how you prioritize customer needs through customized solutions and exceptional service.
• Sustainability and Ethics: If applicable, communicate your environmental initiatives and ethical practices.
Storytelling in Branding
• Company Heritage: Share your company’s history, milestones, and evolution.
• Employee Spotlights: Humanize your brand by featuring stories about your team members.
• Customer Success Stories: Use case studies to illustrate how your solutions have positively impacted clients.
Chapter 4: Building a High-Impact Digital Presence

4.1 Website Optimization Strategies
User Experience (UX) Design
A website with excellent UX encourages visitors to stay longer and engage more deeply.
• Intuitive Navigation: Design clear menus and logical page structures. Use breadcrumbs and search functions to help users find information quickly.
• Mobile Responsiveness: With increasing mobile device usage, ensure your site adapts seamlessly to different screen sizes.
• Accessibility Compliance: Follow WCAG guidelines to make your site accessible to users with disabilities, enhancing usability for all.
• Fast Loading Speeds: Optimize images and code to ensure pages load quickly, reducing bounce rates.
• Engaging Visuals: Use high-quality images, infographics, and videos to enhance engagement.
Search Engine Optimization (SEO)
SEO increases your website’s visibility on search engines, driving organic traffic.
• Keyword Research: Identify relevant keywords and phrases your target audience uses. Tools like Google Keyword Planner and SEMrush can assist.
• On-Page SEO: Optimize title tags, meta descriptions, headers, and image alt texts with target keywords.
• Quality Content Creation: Regularly publish valuable content that answers your audience’s questions and positions your company as an industry expert.
• Link Building: Earn backlinks from reputable sites to improve domain authority.
• Technical SEO: Ensure your website has a clean URL structure, XML sitemap, and is free of crawl errors.
Content Management Systems (CMS)
• Selecting a CMS: Choose a platform like WordPress, Drupal, or Joomla that fits your technical requirements and allows for scalability.
• Regular Updates and Maintenance: Keep your CMS and plugins updated for security and performance enhancements.
4.2 Advanced Content Marketing
Developing a Content Strategy
An effective content strategy aligns with your business goals and customer needs.
• Set Clear Objectives: Define what you want to achieve—brand awareness, lead generation, customer retention, etc.
• Understand Your Audience: Use buyer personas to tailor content topics and formats.
• Content Calendar: Plan content themes, publication dates, and distribution channels in advance.
Types of Content
• Blog Posts: Offer insights on industry trends, how-to guides, and thought leadership pieces.
• Whitepapers and E-books: Provide in-depth analysis or research that requires registration, aiding lead generation.
• Videos and Webinars: Cater to visual learners with product demos, expert interviews, and educational webinars.
• Infographics: Present complex data in a visually appealing and easily digestible format.
• Case Studies: Showcase real-world applications of your products or services and their benefits.
Content Distribution
• Owned Channels: Your website, email newsletters, and social media platforms where you have full control.
• Earned Media: Guest posts, press mentions, and shares from influencers amplify your reach without direct costs.
• Paid Promotion: Use PPC advertising, sponsored content, and social media ads to target specific audiences.
4.3 Social Media Mastery
Platform Optimization
• LinkedIn: Ideal for B2B marketing. Optimize your company page with a compelling description, regular updates, and employee engagement. Participate in industry groups and share valuable content.
• YouTube: Utilize for product demonstrations, tutorials, and thought leadership videos. Optimize video titles, descriptions, and tags for SEO.
• Twitter: Share industry news, engage in conversations using relevant hashtags, and connect with influencers.
• Facebook: While more B2C-focused, it can be useful for community building and sharing company culture.
Content Strategy for Social Media
• Consistent Branding: Use the same logos, colors, and messaging across all platforms.
• Content Mix: Balance promotional posts with educational content, industry news, and interactive posts like polls or Q&A sessions.
• Engagement and Interaction: Respond promptly to comments and messages, fostering a two-way dialogue.
• Analytics Monitoring: Use platform analytics to track engagement, reach, and follower growth, adjusting strategies accordingly.
Chapter 5: Leveraging Email Marketing for Lead Nurturing

5.1 Growing Your Email List
Effective Lead Magnets
• Exclusive Content: Offer downloadable resources like e-books, whitepapers, or industry reports in exchange for email sign-ups.
• Webinars and Events: Host live webinars on relevant topics, requiring registration to capture contact information.
• Free Trials or Demos: Encourage prospects to try your product or service, capturing their details in the process.
Optimizing Opt-In Forms
• Strategic Placement: Position forms on high-traffic pages like the homepage, blog posts, and resource pages.
• Compelling Calls-to-Action (CTAs): Use clear and persuasive language that communicates the value of signing up.
• Minimal Fields: Ask for only essential information to reduce barriers to completion.
• Privacy Assurance: Include statements about data protection to build trust.
5.2 Crafting Effective Email Campaigns
Personalization Techniques
• Segmentation: Divide your email list into groups based on industry, role, behavior, or stage in the buyer’s journey.
• Dynamic Content: Customize email content to reflect the recipient’s interests or past interactions.
• Personalized Subject Lines: Increase open rates by including the recipient’s name or referencing their company.
Email Types
• Welcome Series: Introduce new subscribers to your brand, offerings, and resources.
• Educational Drip Campaigns: Nurture leads with a series of emails that provide valuable information over time.
• Promotional Emails: Announce new products, special offers, or events.
• Re-Engagement Campaigns: Reconnect with inactive subscribers through special incentives or updated content.
Best Practices
• Mobile-Friendly Design: Ensure emails display correctly on all devices.
• Clear and Concise Content: Keep messages focused with a single, clear CTA.
• Testing and Optimization: Use A/B testing for subject lines, send times, and content to improve performance.
• Compliance: Adhere to regulations like CAN-SPAM, GDPR, and CASL by including unsubscribe options and respecting user preferences.
5.3 Analyzing Email Performance
Interpreting Metrics
• Open Rate: Measures the effectiveness of your subject lines and sender reputation.
• Click-Through Rate (CTR): Indicates how compelling your content and CTAs are.
• Conversion Rate: Assesses how well your email drives desired actions, like signing up for a webinar or requesting a quote.
• Bounce Rate: A high bounce rate may indicate issues with list quality or email deliverability.
• Unsubscribe Rate: Provides insights into content relevance and frequency preferences.
Improving Performance
• Segmentation and Personalization: More targeted emails typically yield higher engagement.
• Content Relevance: Ensure that the content matches the recipient’s interests and needs.
• Frequency Optimization: Find the right balance to stay top-of-mind without overwhelming subscribers.
• Deliverability Monitoring: Use tools to monitor sender reputation and avoid spam filters.
Chapter 6: Maximizing ROI from Trade Shows and Events

6.1 Selecting the Right Events
Aligning Events with Business Goals
• Audience Alignment: Choose events that attract your target demographics and decision-makers.
• Relevance: Ensure the event focuses on your industry or related sectors to maximize networking opportunities.
• Historical Performance: Research past attendee numbers, participant feedback, and ROI statistics.
Budget Considerations
• Cost-Benefit Analysis: Weigh the total costs (booth space, travel, marketing materials) against potential leads and brand exposure.
• Sponsorship Opportunities: Evaluate the benefits of sponsoring parts of the event for increased visibility.
6.2 Pre-Event Planning
Setting Measurable Objectives
• Specific Goals: Define clear, quantifiable targets, such as “generate 150 qualified leads” or “secure 10 meetings with key prospects.”
• Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Establish metrics to evaluate success post-event.
Marketing Material Preparation
• Branded Collateral: Create brochures, flyers, and business cards that reflect your brand identity and messaging.
• Digital Assets: Develop presentations, videos, or interactive displays to engage booth visitors.
• Promotional Items: Offer useful and memorable giveaways that reinforce your brand.
Outreach Campaigns
• Email Invitations: Inform existing contacts and prospects about your participation, encouraging them to visit your booth.
• Social Media Promotion: Use event hashtags and share behind-the-scenes content to build anticipation.
• Appointment Setting: Schedule meetings in advance with key attendees to maximize time at the event.
6.3 Engagement Strategies During the Event
Booth Design and Staffing
• Attractive Layout: Design an open and inviting space with eye-catching visuals and clear messaging.
• Interactive Elements: Incorporate touchscreens, product demos, or VR experiences to engage visitors.
• Knowledgeable Staff: Ensure team members are well-trained, approachable, and capable of addressing technical questions.
Networking Activities
• Workshops and Presentations: Participate in or host educational sessions to showcase expertise.
• Live Demonstrations: Provide hands-on experiences with your products or services.
• Lead Capture Technology: Use digital tools like badge scanners or mobile apps to efficiently collect visitor information.
6.4 Post-Event Follow-Up
Timely Communication
• Personalized Emails: Reference specific conversations or interests expressed by leads during the event.
• Provide Value: Share relevant content, such as whitepapers or case studies, that address their needs.
• Next Steps: Encourage actions like scheduling a meeting, attending a webinar, or trying a demo.
Evaluating Event Success
• Lead Quality Analysis: Assess the potential of each lead based on predefined criteria.
• ROI Calculation: Compare the total investment against the revenue generated or projected from event leads.
• Lessons Learned: Collect feedback from the team to identify what worked well and areas for improvement.
Chapter 7: Implementing Account-Based Marketing (ABM)

7.1 Fundamentals of ABM
What is ABM?
ABM is a strategic approach that focuses on a set of strategically important accounts. Instead of casting a wide net, marketing and sales teams work together to create personalized campaigns aimed at engaging each account.
Benefits of ABM
• Higher ROI: Personalized efforts often result in higher engagement and conversion rates.
• Sales and Marketing Alignment: Collaboration enhances efficiency and effectiveness.
• Customer Experience: Tailored interactions improve customer satisfaction and loyalty.
7.2 Customizing Marketing Efforts
Personalized Content Creation
• Account-Specific Messaging: Develop value propositions that address the unique challenges and goals of each account.
• Customized Collateral: Create whitepapers, case studies, or presentations specifically for the account.
• Dedicated Landing Pages: Direct account-specific campaigns to personalized web pages.
Multi-Channel Outreach
• Direct Mail: Send personalized packages or gifts to key decision-makers.
• Targeted Advertising: Use IP-based targeting or retargeting to display ads to specific accounts.
• Events and Webinars: Invite account stakeholders to exclusive events or workshops.
7.3 Measuring ABM Effectiveness
Key Metrics
• Engagement Levels: Track interactions such as email opens, website visits, content downloads, and event attendance.
• Pipeline Growth: Monitor the increase in opportunities and their progression through the sales funnel.
• Revenue Impact: Attribute closed deals and revenue growth to ABM efforts.
Continuous Improvement
• Feedback Loops: Regularly review results and gather input from sales and marketing teams.
• Data Analysis: Use insights to refine targeting, messaging, and channels.
• Scalability: Assess which successful strategies can be applied to additional accounts.
Chapter 8: Harnessing Advanced Technologies for Marketing

8.1 Marketing Automation
Selecting the Right Platform
• Feature Set: Ensure the platform offers necessary functionalities like email automation, lead scoring, and analytics.
• Integration Capabilities: It should integrate seamlessly with your CRM and other tools.
• Ease of Use: A user-friendly interface encourages adoption among team members.
Implementing Automation
• Lead Nurturing Campaigns: Set up automated workflows to guide prospects through the buyer’s journey.
• Behavioral Triggers: Automate responses based on actions like email clicks or website visits.
• Performance Monitoring: Use analytics to measure campaign effectiveness and adjust strategies.
8.2 Artificial Intelligence (AI) Applications
Enhancing Customer Interactions
• Chatbots: Implement AI-powered chatbots for 24/7 customer support and lead qualification.
• Predictive Personalization: Use AI to analyze behavior and personalize content or product recommendations.
• Sentiment Analysis: Monitor social media and customer feedback to gauge brand perception.
Operational Efficiency
• Data Analysis: AI can process large datasets to uncover trends and insights faster than manual analysis.
• Content Generation: AI tools can assist in creating content outlines or drafting emails.
8.3 Virtual and Augmented Reality
Engaging Product Demonstrations
• Virtual Showrooms: Allow customers to explore products in a simulated environment.
• AR Applications: Enable customers to visualize products in their own space using mobile devices.
Training and Development
• Employee Training: Use VR for immersive training experiences, improving retention and engagement.
• Customer Education: Provide interactive tutorials to help clients understand complex products.
8.4 Internet of Things (IoT)
Smart Manufacturing and Marketing
• Data Collection: Use IoT devices to gather real-time data on product performance and customer usage.
• Predictive Maintenance: Offer services that anticipate and address issues before they occur.
• Enhanced Product Development: Leverage data insights to inform future product improvements.
Chapter 9: Strengthening Customer Relationships

9.1 Excellence in Customer Service
Building a Customer-Centric Culture
• Training Programs: Equip employees with the skills and knowledge to deliver exceptional service.
• Empowerment: Allow employees to make decisions that benefit the customer, fostering accountability.
• Feedback Mechanisms: Encourage customers to provide feedback and act on it promptly.
Multichannel Support
• Consistency Across Channels: Provide seamless support via phone, email, live chat, and social media.
• Proactive Outreach: Anticipate customer needs and offer assistance before issues arise.
9.2 After-Sales Engagement
Customer Success Programs
• Dedicated Account Managers: Offer personalized support and build stronger relationships.
• Regular Check-Ins: Schedule periodic reviews to assess satisfaction and uncover additional needs.
• Upselling and Cross-Selling: Present relevant products or services that add value.
9.3 Building Loyalty
Creating Brand Advocates
• Referral Programs: Incentivize customers to recommend your company to others.
• Exclusive Communities: Develop forums or groups for customers to share experiences and insights.
• Recognizing Loyalty: Offer rewards or recognition for long-term customers.
9.4 Handling Complaints and Issues
Effective Resolution Strategies
• Active Listening: Fully understand the customer’s issue without interruption.
• Timely Response: Address complaints promptly to prevent escalation.
• Follow-Up: Ensure the customer is satisfied with the resolution and reaffirm your commitment to their success.
Chapter 10: Data-Driven Marketing and Analytics
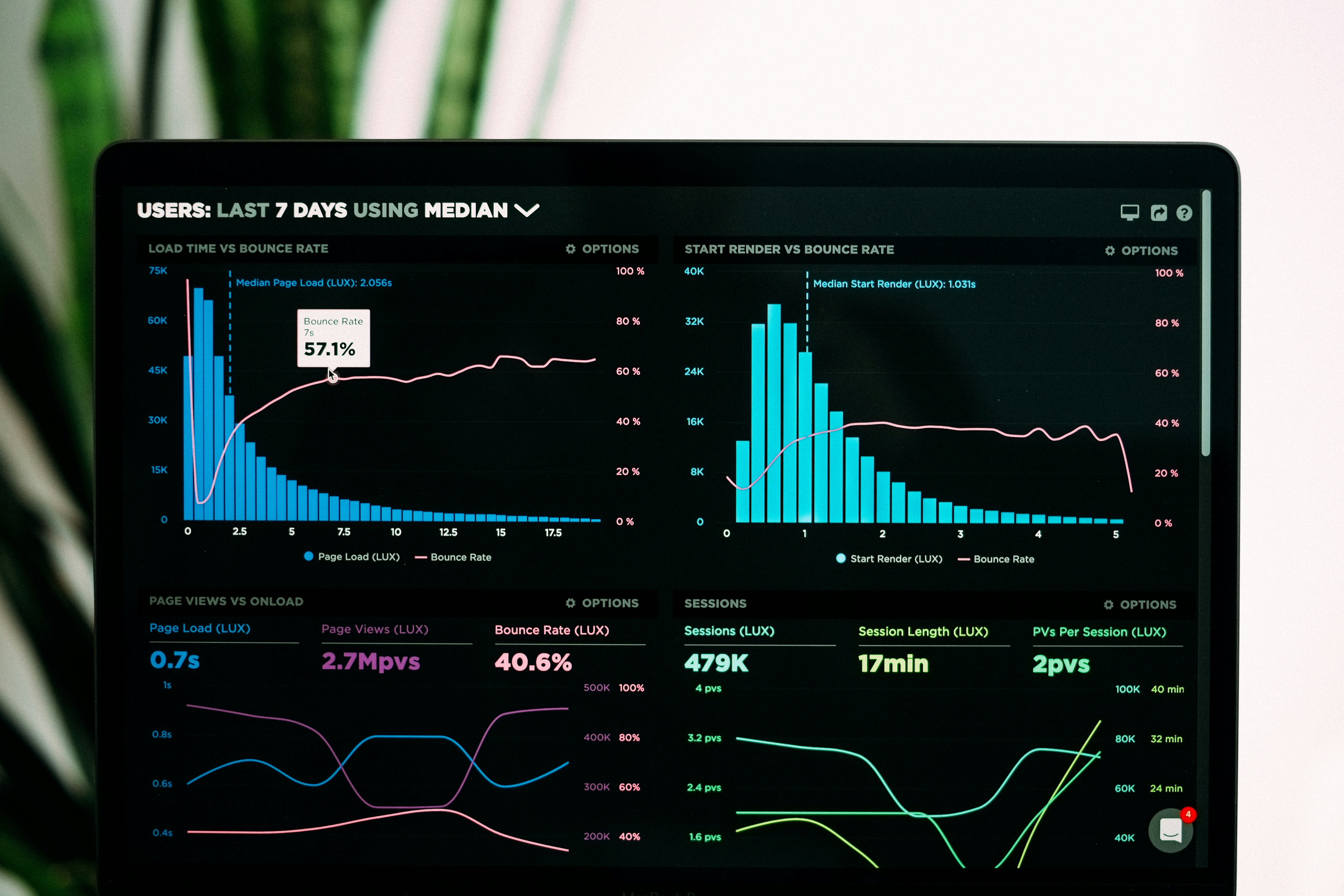
10.1 Establishing a Data Infrastructure
Integrating Systems
• Unified Data Management: Centralize data from various sources (CRM, ERP, marketing platforms) for a holistic view.
• APIs and Middleware: Use technology solutions to facilitate data flow between systems.
Data Quality Management
• Regular Audits: Check for inaccuracies, duplicates, and outdated information.
• Data Cleansing: Implement processes to maintain data integrity.
• Compliance: Ensure data handling practices meet regulatory standards like GDPR.
10.2 Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Selecting Relevant KPIs
• Marketing Metrics: Track metrics like CPL (Cost Per Lead), CPA (Cost Per Acquisition), and MQL (Marketing Qualified Leads).
• Sales Metrics: Monitor conversion rates, average deal size, and sales cycle length.
• Customer Metrics: Measure customer lifetime value (CLV), retention rates, and NPS (Net Promoter Score).
Monitoring and Reporting
• Dashboards: Use visualization tools to monitor KPIs in real-time.
• Regular Reporting: Schedule reports for stakeholders to review performance and make data-driven decisions.
10.3 Advanced Analytics Techniques
Predictive Analytics
• Sales Forecasting: Use historical data to predict future sales trends.
• Lead Scoring Models: Identify high-potential leads based on behavior and engagement.
• Churn Prediction: Anticipate customer attrition and implement retention strategies.
Data Visualization
• Interactive Reports: Allow users to drill down into data for deeper insights.
• Customized Views: Tailor dashboards for different roles within the organization.
Chapter 11: Ensuring Compliance and Ethical Marketing

11.1 Regulatory Compliance
Data Protection Laws
• GDPR and CCPA Compliance: Implement policies for data consent, access, and deletion requests.
• Data Security: Use encryption and secure storage solutions to protect customer data.
Industry Regulations
• Quality Standards: Adhere to certifications like ISO 9001 for quality management.
• Environmental Regulations: Comply with laws related to emissions, waste management, and resource usage.
11.2 Ethical Marketing Practices
Transparency and Honesty
• Truthful Advertising: Avoid misleading claims or exaggerations.
• Clear Terms and Conditions: Ensure customers understand pricing, warranties, and return policies.
Social Responsibility
• Sustainability Initiatives: Implement eco-friendly practices and communicate them to customers.
• Community Engagement: Participate in local events or charitable activities.
11.3 Crisis Management
Developing a Crisis Plan
• Risk Assessment: Identify potential crises and their impact.
• Communication Strategy: Prepare templates and guidelines for internal and external communication.
• Response Team: Assign roles and responsibilities for crisis management.
Execution During a Crisis
• Timely Updates: Provide accurate information promptly.
• Empathy and Accountability: Show concern and take responsibility where appropriate.
• Post-Crisis Evaluation: Analyze response effectiveness and update plans accordingly.
Chapter 12: Training and Empowering Your Team

12.1 Employee Development
Continuous Learning Culture
• Training Programs: Offer courses on industry trends, technology, and soft skills.
• Mentorship Opportunities: Pair less experienced employees with seasoned professionals.
• Performance Reviews: Provide constructive feedback and set development goals.
12.2 Encouraging Innovation
Idea Sharing Platforms
• Suggestion Boxes: Create channels for employees to submit ideas.
• Innovation Challenges: Host competitions to solve company challenges.
• Recognition Programs: Reward innovative contributions.
12.3 Sales and Marketing Alignment
Collaborative Processes
• Shared Goals: Align KPIs to encourage teamwork.
• Regular Meetings: Facilitate communication and strategy alignment.
• Integrated Tools: Use platforms that support both sales and marketing functions.
Chapter 13: Scaling Your Marketing Efforts

13.1 Budget Allocation
Strategic Investment
• Performance-Based Budgeting: Allocate funds to high-performing channels.
• Technology Adoption: Invest in tools that enhance efficiency and scalability.
13.2 Global Market Expansion
Market Entry Strategies
• Market Research: Analyze potential markets for demand, competition, and cultural fit.
• Local Partnerships: Collaborate with local businesses to navigate regulatory environments and cultural nuances.
• Localization: Adapt products, services, and marketing materials to meet local preferences.
13.3 Partnership Development
Building Strategic Alliances
• Complementary Partnerships: Team up with companies offering complementary products or services.
• Joint Ventures: Share resources and expertise for mutual benefit.
• Co-Marketing Opportunities: Expand reach through collaborative marketing efforts.
Conclusion
The manufacturing industry’s landscape is rapidly evolving, and companies must adapt their marketing strategies to stay competitive. By embracing digital transformation, understanding your target audience, and leveraging advanced technologies, you can create a robust marketing framework that drives growth and builds lasting customer relationships.
At the heart of successful marketing lies a deep understanding of your customers and a commitment to delivering exceptional value. This guide provides the foundation, but continuous learning and adaptation are key to thriving in the dynamic manufacturing sector.
Your journey toward marketing excellence starts today. Whether you need assistance in developing a comprehensive marketing strategy or implementing specific initiatives, our team is here to support you. Contact us now to discover how we can collaborate to elevate your manufacturing company’s marketing efforts and achieve your business objectives.
Fello Agency is a marketing firm that specializes in providing tailored marketing solutions for manufacturing companies. They focus on helping manufacturers enhance their marketing efforts to reach a wider audience, generate quality leads, and increase sales. Recognizing the unique challenges and opportunities within the manufacturing sector, Fello Agency offers services designed to bridge the gap between traditional manufacturing practices and modern marketing techniques.
